Mars Express space orbiterThe European Space Agency has obtained evidence of the presence of liquid water under the layers of ice and dust in one of the regions of the South Pole of Mars. On the opening of the official website writes the European Space Agency.
The fact that once on the surface of the Redthe planets had been in liquid water for a long time scientists hinted at geological features in the form of ancient dried riverbeds, canals and other geological structures visible from orbiters. In addition, in the tandem with orbital probes on the surface of the planet work several rovers, which also find evidence in favor of the "raw" history of the Red Planet. It is indicated at least by the presence of certain types of minerals that can be formed only under the conditions of the presence of water pressure.
According to scientists, during the existence of Mars(about 4.6 billion years) its climate has changed significantly and today water in liquid form cannot linger on the surface of the planet. Therefore, the researchers decided to see whether there is liquid water under it.
Planetologists have long been inclined to probabilitythe presence of liquid water under the base of the ice caps at the poles. In the end, we know that the freezing point can drop under the pressure of the overlying glacier. In addition, the presence of salts on Mars is able to further lower the freezing point, allowing water to remain in a liquid state even at a negative temperature.
Until recently, data from installed onThe Mars Express of the European Space Agency's specialized radar for sounding the ionosphere and the deep layers of the Martian surface (MARSIS) looked unconvincing to scientists. In order to confirm their assumptions, the researchers had to work hard on how to maximize its effectiveness and give the opportunity to collect data in as high a resolution as possible in this case.
Penetrating radar uses the send methodsignals through the surface of the planet and calculates the time it takes to reflect the signal and return it to the spacecraft. The peculiarity of the chemical properties of elements that are in the path of motion of a signal changes it. The signal can be either dimmer, which may indicate, for example, the presence of hard rocks in its path, or more clear or even amplified, which will indicate a high reflectivity of the element that reflected it. Thanks to this, scientists can determine what is under the surface of the planet.

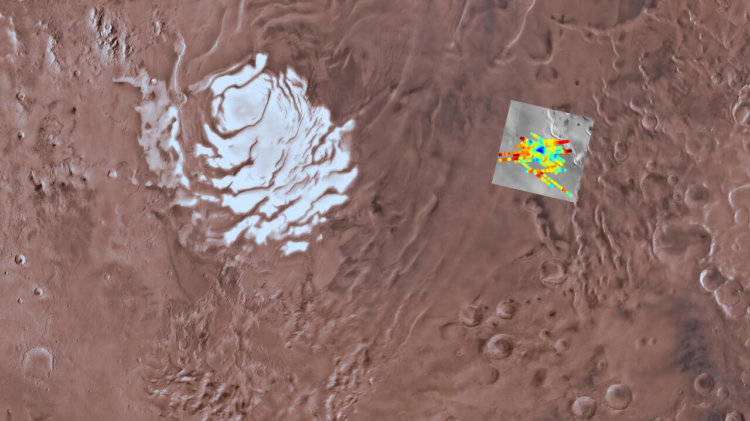
Map of the Southern Plateau and the area in which the research was conducted
Sounding a region about 200 kilometers wideusing MARSIS showed that the surface of the South Pole of Mars is covered with several layers of ice and dust and a depth of about 1.5 kilometers. A particularly powerful signal reflection enhancement was recorded under layered sediments within a 20-kilometer zone at a depth of about 1.5 kilometers. After analyzing the properties of the reflected signal and examining the composition of layered sediments, as well as the expected temperature profile below the surface of this area, the scientists came to the conclusion that MARSIS found a pocket with a lake of liquid water under the surface. Scientists note that the device could not determine how deep the lake could be, but according to rough estimates its depth should be at least several tens of centimeters (this should be the layer of water that MARSIS could see it).

Image from the radar MARSIS
“It really qualifies as a body of water. The lake, not some kind of melt water, fills some space between the rock and ice, as it happens in certain areas on Earth, ”commented Professor Roberto Orosei of the Italian Institute of Astrophysics, who heads the study.

Theoretically signal amplification in whichthey suspect a lake, may produce a layer of frozen carbon dioxide or simply low-temperature water ice, but the authors reject these assumptions, since these options are not well consistent with the observations.
“The only possible explanation for what we see is liquid water,” said Orosei.
"With the help of MARSIS, we found out that there isliquid water, it is salty and is in contact with bottom sediments. Ingredients so that life could exist there, in place, and more MARSIS can not say anything, he cannot answer the question of whether there is life there, ”added Enrico Flamini, representing the Italian Space Agency.
"Assumptions about the presence of liquid water underMars polar caps appeared many years ago. However, it has not yet been possible to confirm or refute them, as it was not possible to detect persistent accumulations of liquid water on Mars, because the data collected were of very poor quality, ”adds Andrea Cicchetti, co-author of the study.
With the help of the radar, only a few percent of the Southern Plateau were surveyed, and its characteristics make it possible to see only fairly large accumulations of water.
“This is just one small area. Just imagine that under the surface of Mars there can be many such underground lakes with water. ”